Rotate Vector To Orthogonal Direction
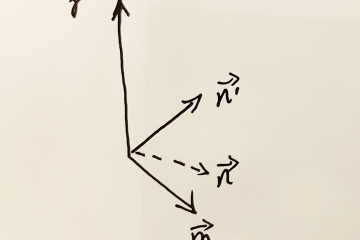
Rotate Vector To Orthogonal Direction Just like in the picture, we will rotate vector to which is orthogonal to the neighbor . The vector is the cross product of and . #include <iostream> #include “point.hpp” int main() { Point m( Read more…